Log Normal Distribution
Where do you meet this distribution?
- Finance, Economics : Change of stock price
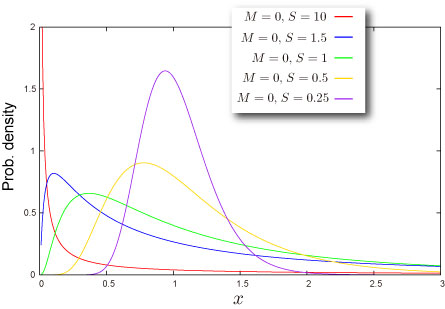
Shape of Distribution
Basic Properties
-
Two parameters are required (How can you get these).
-
Continuous distribution defined on semi-bounded range
-
This distribution is always asymmetric.
Probability
-
Cumulative distribution function
where
is cumulative distribution function of standard normal distribution. -
where
is probability density function of standard normal distribution. -
How to compute these on Excel.
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.5 | Value for which you want the distribution |
| 3 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 4 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 5 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 6 | =NTLOGNORMDIST(A2,A3,A4,TRUE) | Cumulative distribution function for the terms above |
| 7 | =NTLOGNORMDIST(A2,A3,A4,FALSE) | Probability density function for the terms above |
- Function reference : NTLOGNORMDIST
Quantile
-
Inverse function of cumulative distribution function
where
is cumulative distribution function of standard normal distribution. -
How to compute this on Excel.
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.7 | Probability associated with the distribution |
| 3 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 4 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 5 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 6 | =NTLOGNORMINV(A2,A3,A4) | Inverse of the cumulative distribution function for the terms above |
Characteristics
Mean -- Where is the "center" of the distribution? (Definition)
-
Mean of the distribution is given as
where
-
How to compute this on Excel
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 3 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 4 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 5 | =NTLOGNORMMEAN(A2,A3) | Mean of the distribution for the terms above |
- Function reference : NTLOGNORMMEAN
Standard Deviation -- How wide does the distribution spread? (Definition)
-
Variance of the distribution is given as
where
Standard Deviation is a positive square root of Variance.
-
How to compute this on Excel
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 3 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 4 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 5 | =NTLOGNORMSTDEV(A2,A3) | Standard deviation of the distribution for the terms above |
- Function reference : NTLOGNORMSTDEV
Skewness -- Which side is the distribution distorted into? (Definition)
-
Skewness of the distribution is given as
where
-
How to compute this on Excel
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 3 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 4 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 5 | =NTLOGNORMSKEW(A2,A3) | Skewness of the distribution for the terms above |
- Function reference : NTLOGNORMSKEW
Kurtosis -- Sharp or Dull, consequently Fat Tail or Thin Tail (Definition)
-
Kurtosis of the distribution is given as
where
-
How to compute this on Excel
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 3 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 4 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 5 | =NTLOGNORMKURT(A2,A3) | Kurtosis of the distribution for the terms above |
- Function reference : NTLOGNORMKURT
Random Numbers
-
Random number x is generated by inverse function method, which is for uniform random U,
where\
-
How to generate random numbers on Excel.
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data | Description |
| 2 | 0.1 | Value of parameter M |
| 3 | 2 | Value of parameter S |
| 4 | Formula | Description (Result) |
| 5 | =NTRANDLOGNORM(100,A2,A3,0) | 100 log normal deviates based on Mersenne-Twister algorithm for which the parameters above |
Note The formula in the example must be entered as an array formula. After copying the example to a blank worksheet, select the range A7:A106 starting with the formula cell. Press F2, and then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER.
- Function reference : NTRANDLOGNORM
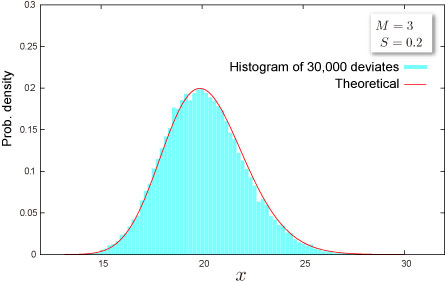
NtRand Functions
- If you already have parameters of the distribution
- Generating random numbers based on Mersenne Twister algorithm: NTRANDLOGNORM
- Computing probability : NTLOGNORMDIST
- Computing mean : NTLOGNORMMEAN
- Computing standard deviation : NTLOGNORMSTDEV
- Computing skewness : NTLOGNORMSKEW
- Computing kurtosis : NTLOGNORMKURT
- Computing moments above at once : NTLOGNORMMOM
- If you know mean and standard deviation of the distribution
- Estimating parameters of the distribution:NTLOGNORMPARAM